What to look for in a Wi-Fi router
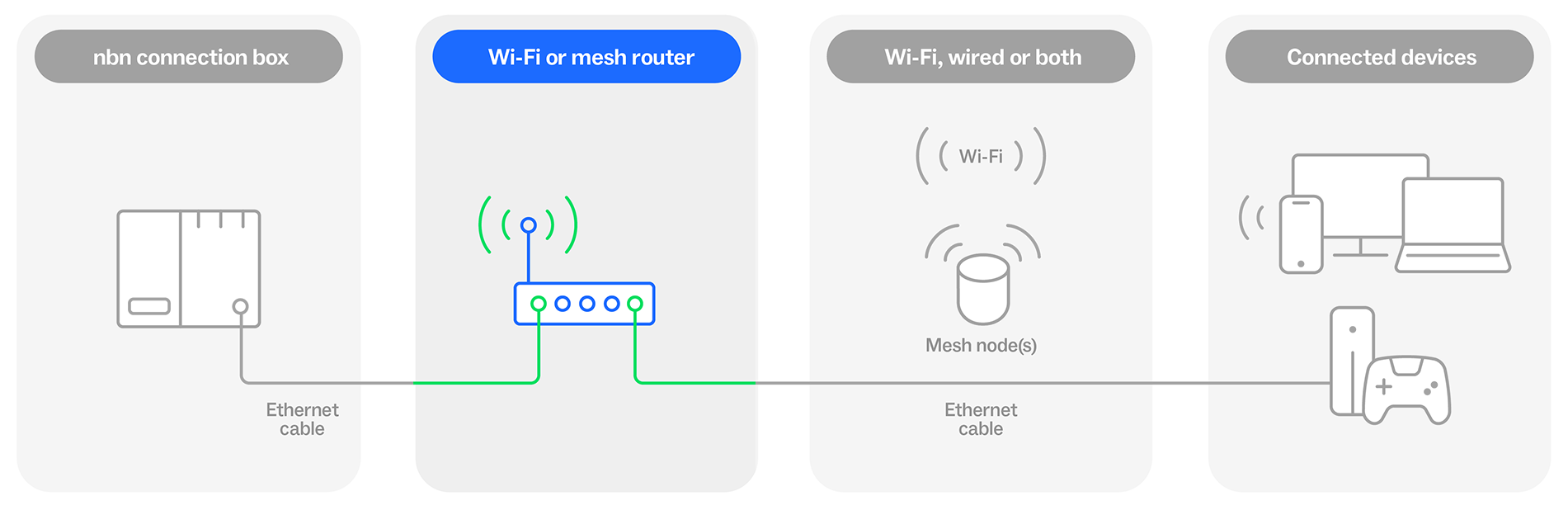
Your Wi-Fi router is a vital part of your online experience, sending and receiving traffic from your connected devices to the nbn® network.
So when was the last time you thought about what you need in a Wi-Fi router, its age, or whether it suits your needs?
What are Wi-Fi generations and why do they matter
Just like mobile networks have different generations (like 4G and 5G), so too does your Wi-Fi router. Each time a new generation is released, it makes way for faster speeds, and the potential for an enhanced experience.
An older router might only support slower Wi-Fi speeds, meaning it won’t be able to reach the higher speeds available on some nbn powered plans.
What speed does your router’s Wi-Fi generation support?
Generally, the higher the generation number, the faster the data connection. If you have a Wi-Fi 5 router or if you received your router before 2019, it might not be capable of achieving the speeds available with selected plans. Please see the table below for detail.
| Wi-Fi generation | Typical maximum Wi-Fi speeds | Approximate year of release |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) |
Over 1Gbps | 2024 |
| Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) |
Up to 1Gbps | 2019 |
| Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) |
Up to 500Mbps | 2013 |
| Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) |
Up to 100Mbps | 2009 |
This table is intended to be a guide only. Device capabilities may vary by internet provider or manufacturer. We recommend speaking with your internet provider about the performance of your Wi-Fi router and your nbn plan.
If you have updated your wifi-router recently you can recycle your old Wi-Fi router and electronic equipment responsibly, check with your local council, electronic retailer or speak to your internet provider, as many offer local and free e-waste recycling programs, or visit recyclemate.com.au.
Mesh coverage: when a single router isn’t enough
A single Wi-Fi router may not provide full coverage for larger or multi-storey properties, leading to slower speeds or dropouts. A Wi-Fi mesh network can help with signal strength by connecting multiple devices called nodes (also known as 'access points’ or ‘satellite nodes’) to your Wi-Fi router, spreading the Wi-Fi signal further.
Benefits to a Wi-Fi mesh network:
- Signal coverage over larger or multi-storey properties
- Signal coverage around materials that can reduce Wi-Fi signal, like thick walls and metal panels
A Wi-Fi mesh network forms a single, streamlined network – unlike Wi-Fi extenders, an older technology that also boosts Wi-Fi signals, but which can cause dropouts by often creating separate networks (SSIDs). Available for over twenty years, Wi-Fi extenders have been surpassed in performance by Wi-Fi mesh networks.
Without a mesh network
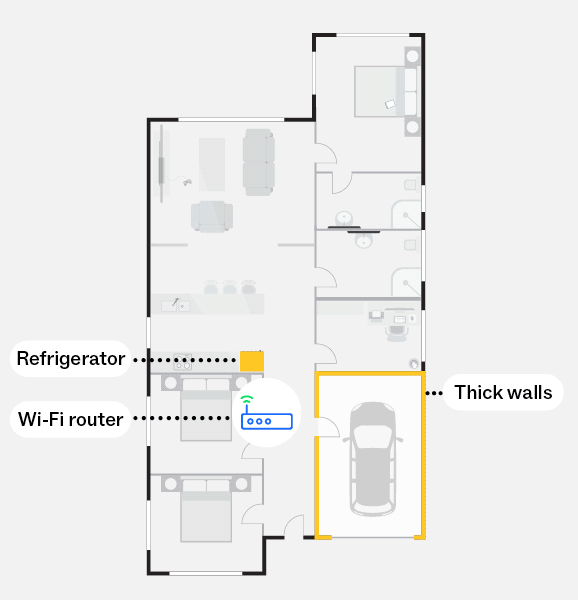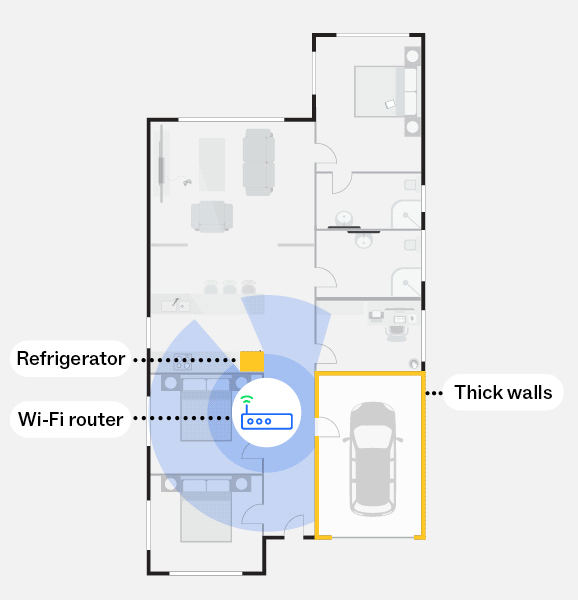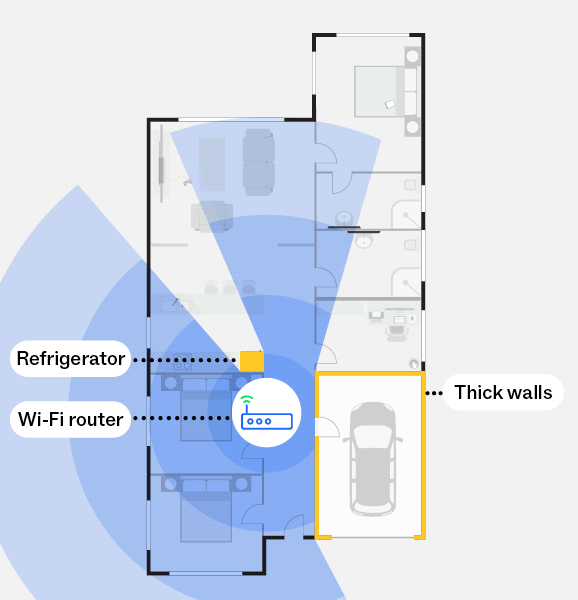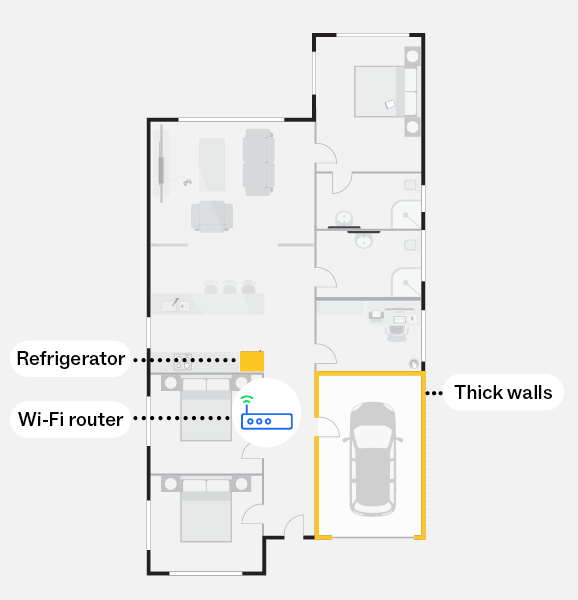
The diagram illustrates how some materials and obstructions such as thick walls and refrigerators can significantly reduce your Wi-Fi signal if they sit between your Wi-Fi router and Wi-Fi connected devices.
With a mesh network
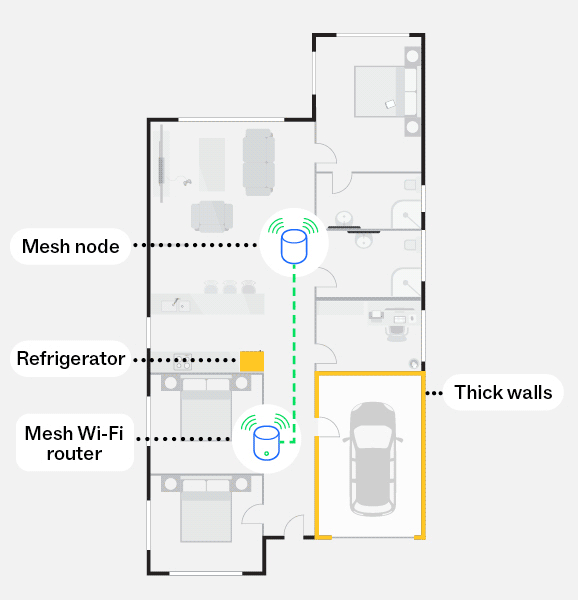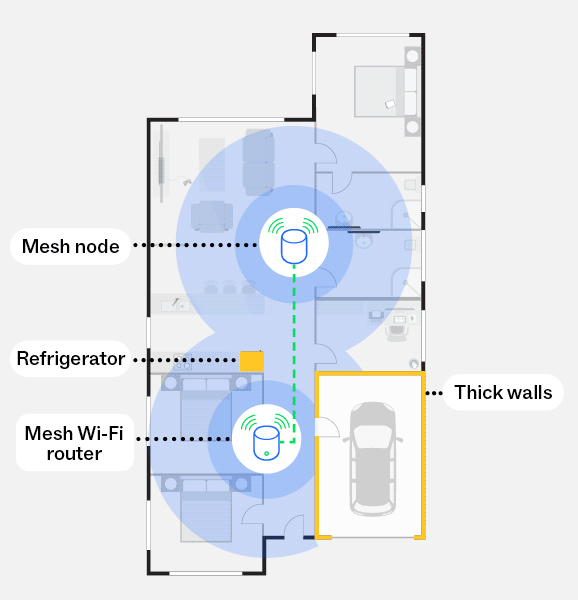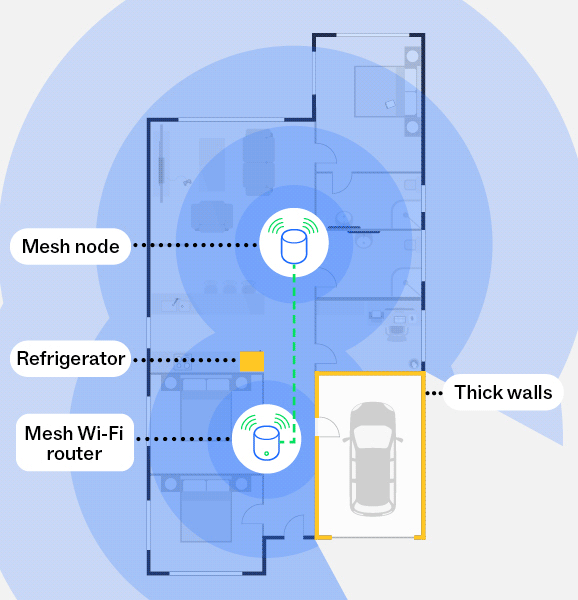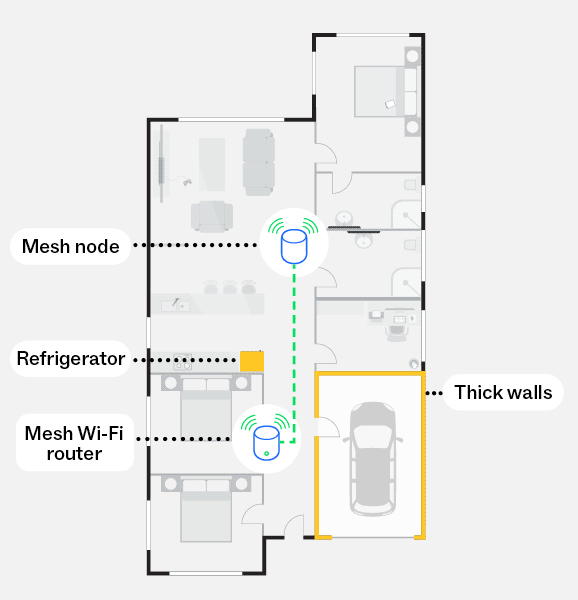
This diagram illustrates how a mesh network, using mesh nodes, can reduce the impacts of obstructions, such as thick walls and refrigerators, and create a stronger Wi-Fi signal throughout your home, including to harder to reach areas.

Why your router ports matter
Your Wi-Fi router is the link between a Wide Area Network (WAN) and your Local Area Network (LAN) with specific ports for each.
The ports on your router come with various capabilities that support different speeds. Devices connected via Ethernet cable will be limited by the speed of the router port, even if the connected device and cable support higher speeds.